What is Big Data?
The Term “Big Data” is Used to Describe :
The large collection of structured and unstructured data, which is difficult to capture, process, store, search and analyse.
Why Hadoop Came Into Existence?
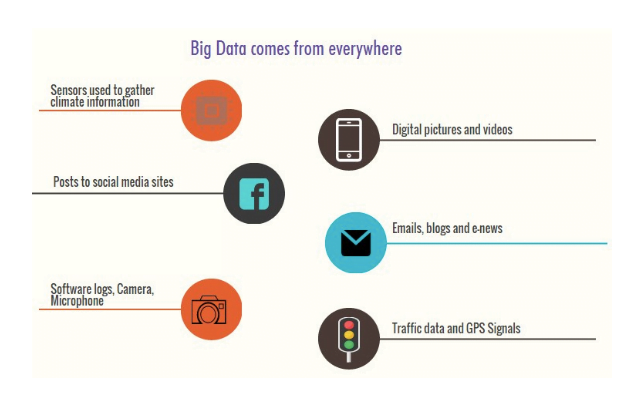
Where Does Big Data Come From ?
The data coming from everywhere for example
- In last 5-10 minutes on Facebook, there is millions of links shared, friend requests, photos uploaded and comments,event invites
- Consumer product companies and retail organizations are monitoring social media like Facebook and Twitter to get an unprecedented view into customer behaviour, preferences, and product perception
- GPS data from mobile devices
- weblogs, emails text, email attachments
- sensors used to gather climate information
- posts to social media sites,
- purchase transaction records and much more
- Terabyte of data generated through Twitter feeds in the last few hours.
Big Data Contains Both Structured and Unstructured Data.
Structured Data
- Data stored in Database tables and spread-sheets.
- Can be easily entered, stored, queries and analysed.
Unstructured Data
- Information that doesn’t reside in a traditional row-column database.
- For example Texts, email, facebook post, audio, video, blog etc.
Large collection of structured and unstructured data stored, aggregated, analyzed and communicated to make better business decisions is called Big Data.
3Vs (volume, variety and velocity) Defining Big Data

The size of available data is growing today exponentially. A text file is a few kilobytes, a sound file is a few megabytes while a full-length movie is a few gigabytes.
More sources of data are getting added on continuous basis. It is very common to have Terabytes and Petabytes of the storage system for enterprises. As the database grows the applications and architecture built to support the data needs to be changed quite often.
Variety Refers To The Number of Types of Data
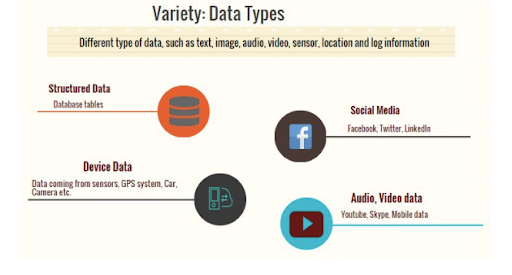
From excel tables and databases, data structure has changed to lose its structure and to add hundreds of formats. Pure text, photo, audio, video, web, GPS data, sensor data, relational data bases, documents, SMS, pdf, flash etc.
Now we no longer have control over the input data format. Structure can no longer be imposed like in the past to keep control over the analysis. As new applications are introduced new data formats come to life. The real world has data in many different formats and that is the challenge we need to overcome with the Big Data.
Why Hadoop is Needed for Big Data?
Now let us see why we need Hadoop for Big Data.
Hadoop Starts Where Distributed Relational Databases Ends.
If relational databases can solve your problem, then you can use it but with the origin of Big Data, new challenges got introduced which traditional database systems couldn’t solve fully.

Let us understand these challenges in more details.
Challenges For tTraditional Database Management System to Handle Big Data
Challenge 1:
Big Data has a variety of data means along with structured data which relational databases can handle very well, Big Data also includes unstructured data (text, log, audio, streams, video stream, sensor, GPS data). The traditional databases require the database schema to be created in ADVANCE to define the data how it would look like which makes it harder to handle Big unstructured data.
Challenge 2:
Big Data is getting generated at very high speed. The traditional databases are not designed to handle database insert/update rates required to support the speed at which Big Data arrives or needs to be analyzed.
Challenge 3:
Big Data is data in Zettabytes, growing with an exponential rate. If the data to be processed is in the degree of Terabytes and petabytes, it is more appropriate to process them in parallel independent tasks and collate the results to give the output. Traditional database approaches can’t handle this.
To handle these challenges a new framework came into existence, Hadoop.
Hadoop is a framework to handle vast volumes of structured and unstructured data in a distributed manner.
Hadoop is Not a Database
It’s very important to know that Hadoop is not a replacement for a traditional database.
Unlike RDBMS where you can query in real-time, the Hadoop process takes time and doesn’t produce immediate results. Hadoop is a computing architecture, not a database.